Just add new special input key for KubeInvaders. Press ‘n’ to jump between namespaces!
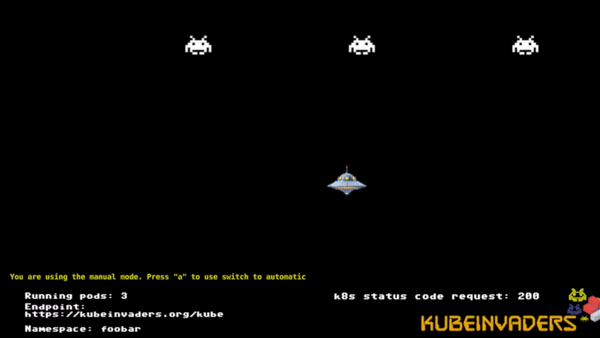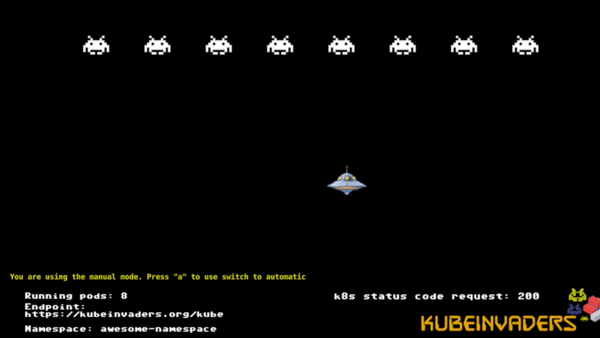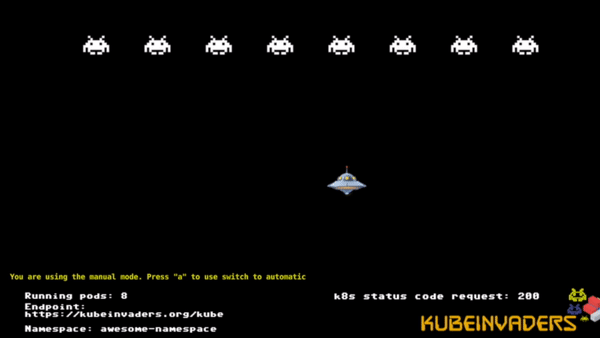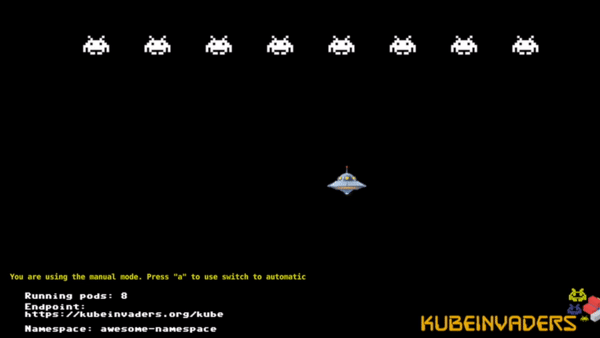
Recently I released a gamified chaos engineering tool for Kubernetes (it has been added in https://github.com/dastergon/awesome-chaos-engineering some days ago) and I would like deploy it on Openshift 4.1.
First of all, follow these two guides:
Openshift 4 Install Experience
A today, for trying Openshift 4 the best choise is by using AWS. The openshift-install-linux utility installs a ready to use cluster through Terraform.
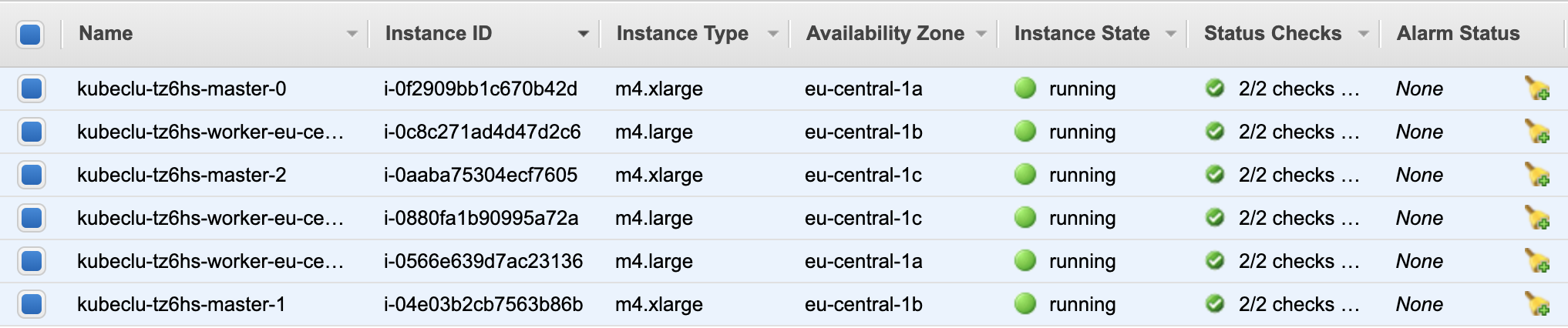
The installation is very easy and after the execution of openshift-install-linux-amd64 I had just to follow instructions for connecting to my new Openshift cluster.
time="2019-05-02T10:58:45Z" level=debug msg="OpenShift console route is created" time="2019-05-02T10:58:45Z" level=info msg="Install complete!" time="2019-05-02T10:58:45Z" level=info msg="Run 'export KUBECONFIG=/root/auth/kubeconfig' to manage the cluster with 'oc', the OpenShift CLI." time="2019-05-02T10:58:45Z" level=info msg="The cluster is ready when 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p xxxx succeeds (wait a few minutes)." time="2019-05-02T10:58:45Z" level=info msg="Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.kubeclu.kubeinvaders.io" time="2019-05-02T10:58:45Z" level=info msg="Login to the console with user: kubeadmin, password: xxxx"
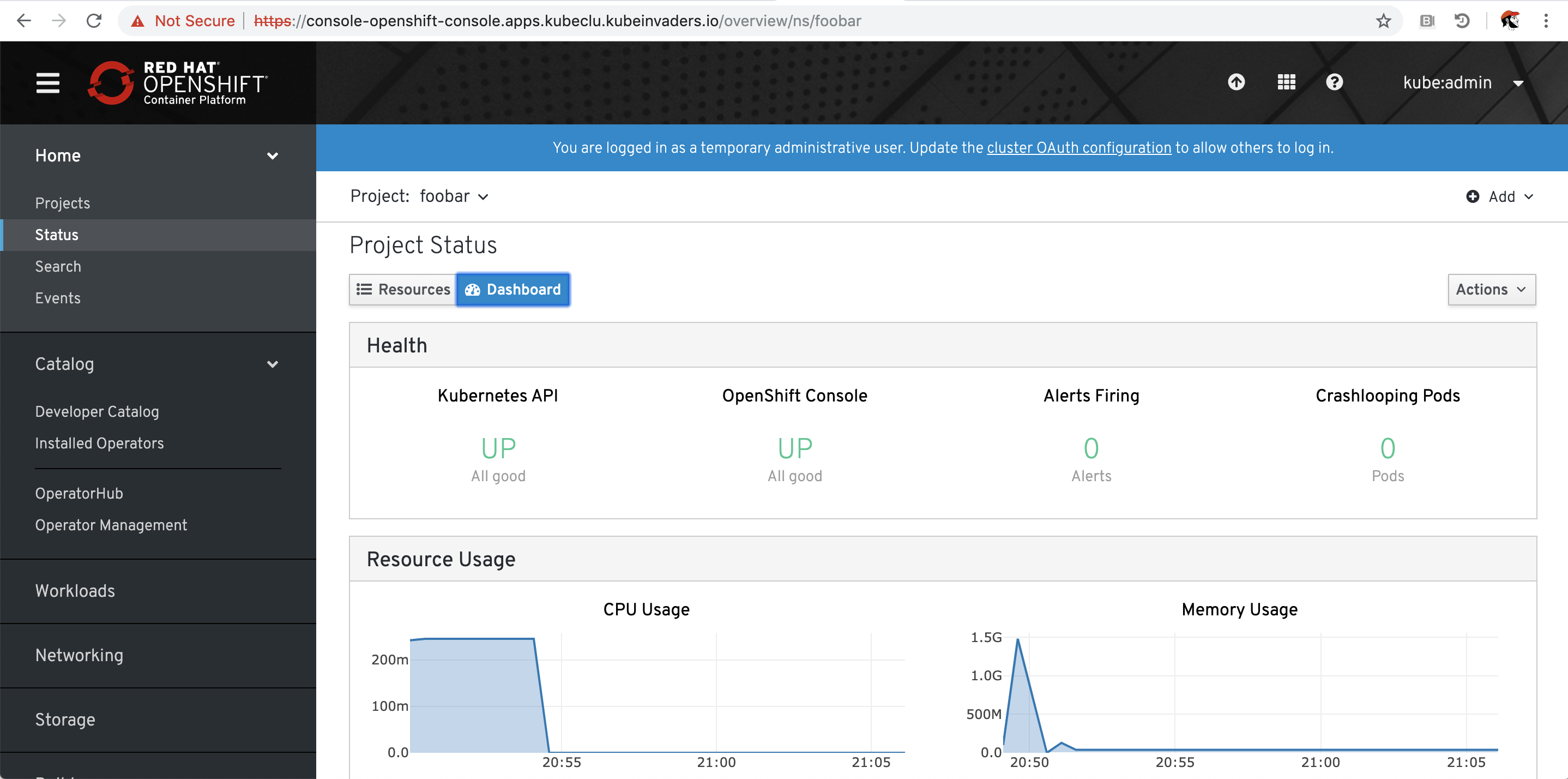
Before to deploy KubeInvaders create a sample namespace in which run, for example, NodeJS applications. You can deploy it directly from the Openshift catalog.
Let’s install KubeInvaders.
# Clone KubeInvaders git clone https://github.com/lucky-sideburn/KubeInvaders.git
# Do the following commands. # Same and updated guide on https://github.com/lucky-sideburn/KubeInvaders#install-kubeinvaders-on-openshift # The namespace you want to stress TARGET_NAMESPACE=foobar # Choose route host for your kubeinvaders instance. ROUTE_HOST=kubeinvaders.apps.kubeclu.kubeinvaders.io # Please add your source ip IP_WHITELIST. This will add haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist in KubeInvaders route # https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.9/architecture/networking/routes.html#whitelist IP_WHITELIST="10.10.10.10" oc new-project kubeinvaders --display-name='KubeInvaders' oc create sa kubeinvaders -n kubeinvaders oc create sa kubeinvaders -n $TARGET_NAMESPACE oc adm policy add-role-to-user edit -z kubeinvaders -n $TARGET_NAMESPACE TOKEN=$(oc describe secret -n $TARGET_NAMESPACE $(oc describe sa kubeinvaders -n $TARGET_NAMESPACE | grep Tokens | awk '{ print $2}') | grep 'token:'| awk '{ print $2}') oc process -f openshift/KubeInvaders.yaml -p ROUTE_HOST=$ROUTE_HOST -p TARGET_NAMESPACE=$TARGET_NAMESPACE -p TOKEN=$TOKEN | oc create -f -
Open routes and go to KubeInvaders location
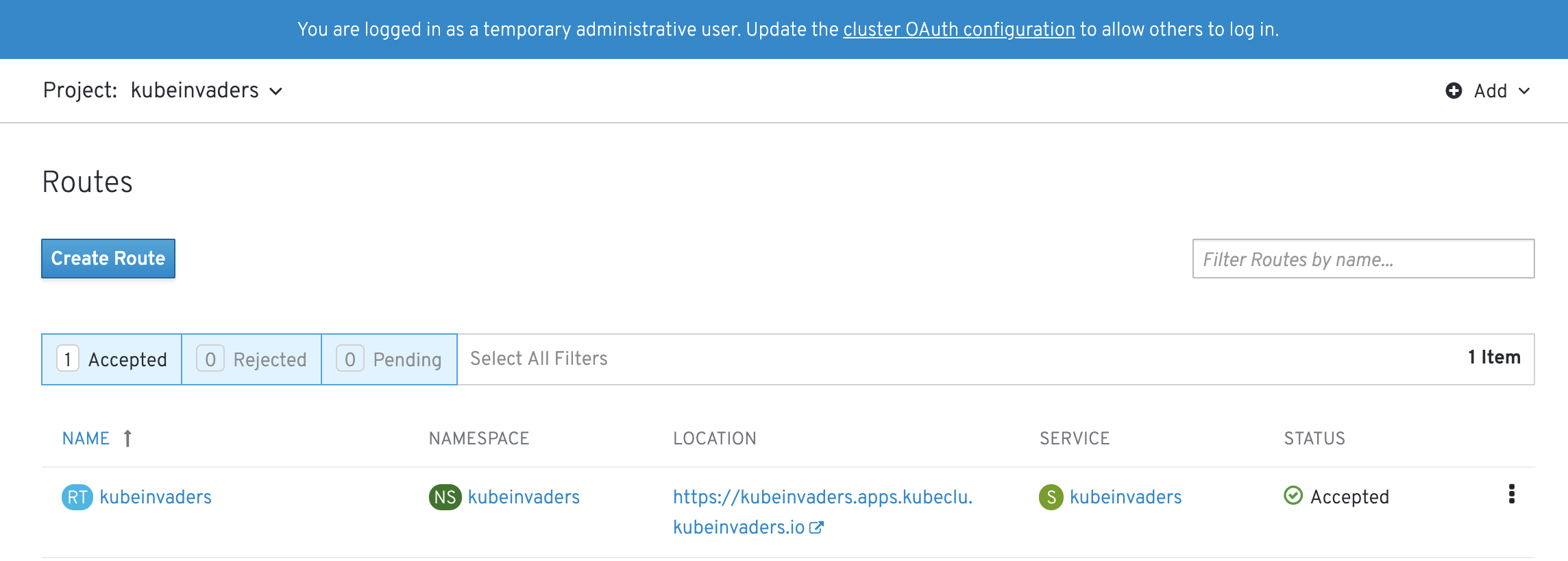
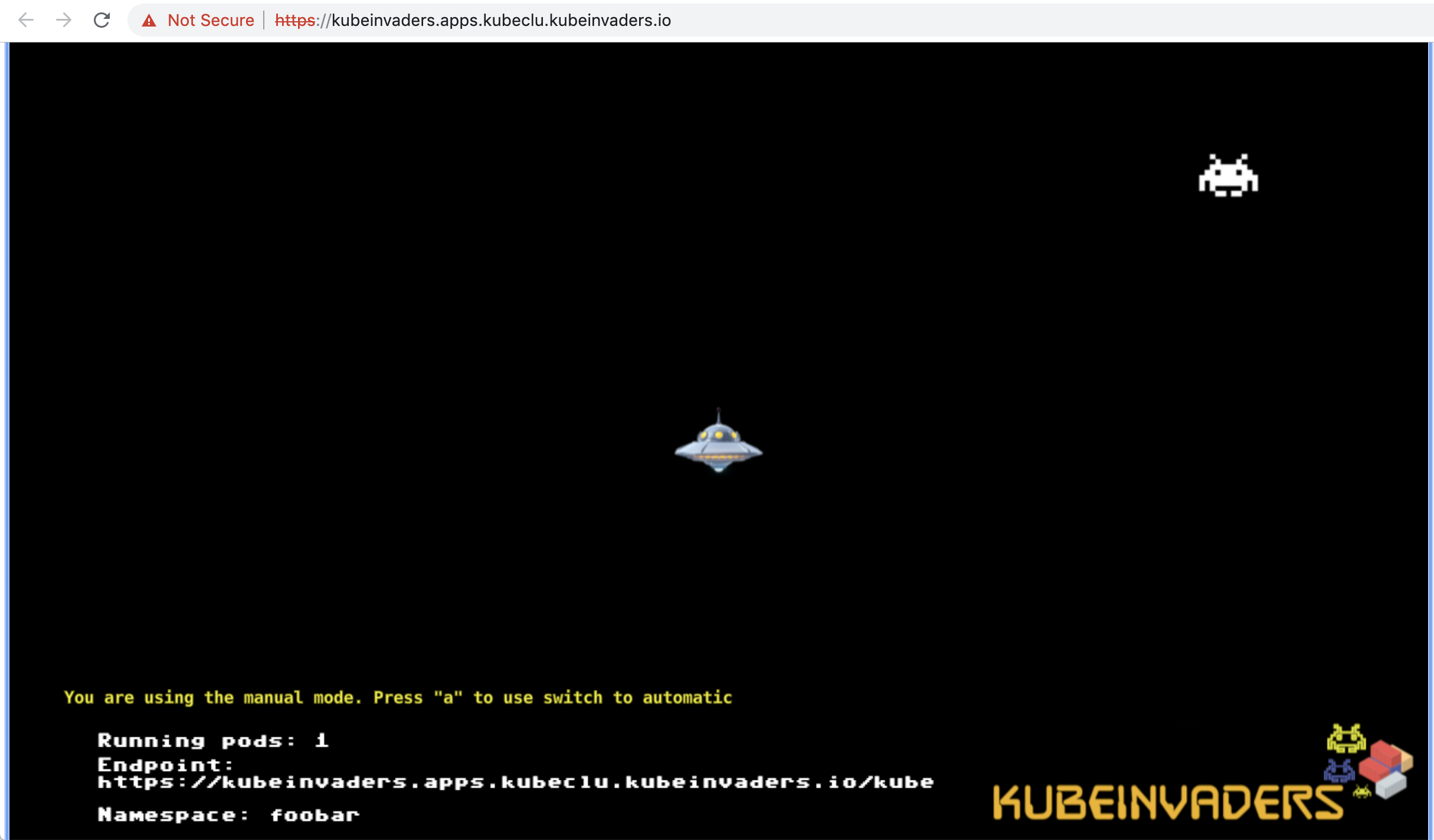
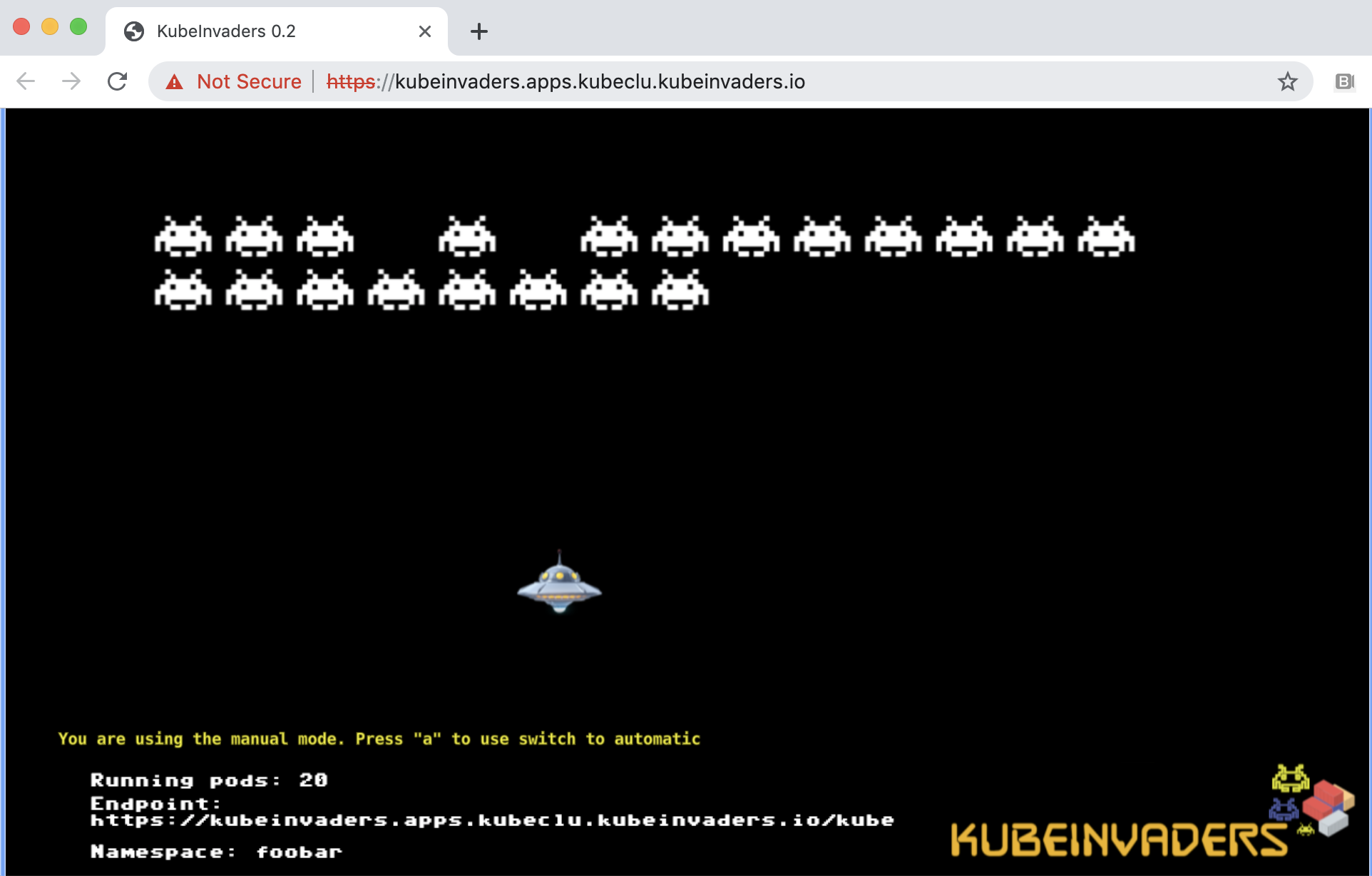
Scale pods of foobar namespace to 20 replicas.
oc scale dc testapp --replicas=20 -n foobar
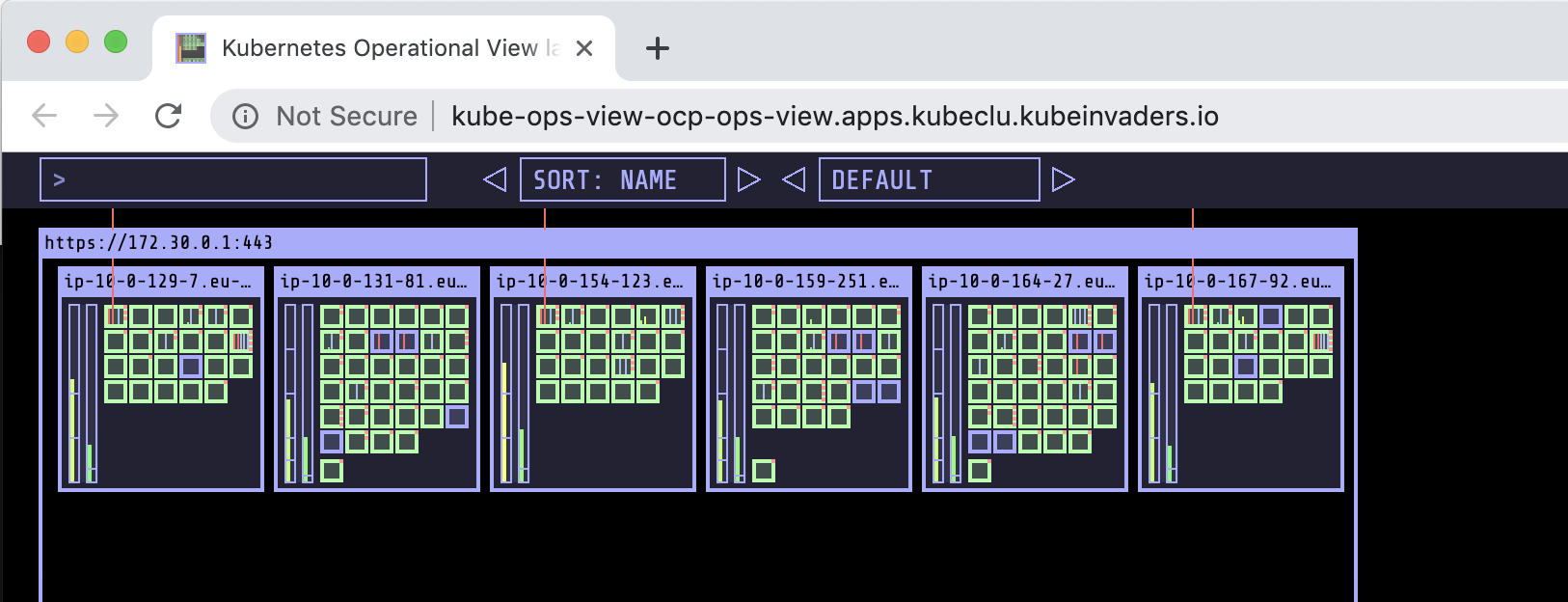
I deployed also https://github.com/hjacobs/kube-ops-view because I find it very cool for watching pods distributed across node workers.
This is how KubeInvaders works with Openshift 4.1.
https://youtu.be/7R9ftgB-JYU
Bye!
